loud breathing through nose
 Is Your Nose Working Against You? 5 Signs of a Deviated Septum – Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic
Is Your Nose Working Against You? 5 Signs of a Deviated Septum – Health Essentials from Cleveland ClinicWe use cookies and similar tools to give you the best experience on the website. By using our site, you accept our . We have a limited supply of COVID-19 vaccines and offer eligible patients based on state and federal guidelines. Please don't call us for a vaccine date. We are notifying patients individually when they can schedule. so we can notify him. More information about it. Explore the health of NYU Langone Conditions we deal with Explore our approach to diagnose and treat adults and children. Our history NYU Langone Health is one of the nation's leading academic medical centers. Diagnosing the Stridor in AdultsThe stridor, or noisy breathing, is caused by a narrow or partially blocked airway, the passage that connects the mouth to the lungs. This results in sounds that sibil or whistles that can be acute and audible when a person inhales, exhales or both. NYU Langone otolaryngology specialists — also known as ear, nose, and throat doctors, or ENT — often diagnose the cause of the stridor during a physical examination. If more diagnostic tests are needed, doctors use advanced imaging techniques to clearly see the airway. The condition also affects. Because your airways are narrower, even a small blockage can interfere with breathing. Causes of Adult Stridor Bilateral vocal cord paralysis is a common cause of stridor in adults. It results from a disturbance in the nervous function in both of the vocal cords, the two small structures in the throat that vibrate and colliden to produce sound, leaving the vocal cord tissues blocking the airway. This causes biphasic stridor, which means noisy breathing symptoms occur when a person inhales and exhales. Bilateral vocal cord paralysis may result from thyroid, thorax, or esophageal surgery, or from being intubated, having an inserted respiratory tube. These procedures can cause scar tissue that interferes with breathing. Subglottitic stenosis, or an unusual narrowing of the airway under the vocal cords, can also cause noisy breathing during inhalation and exhalation. Other causes of the adult stridor include a narrowing of the trachea called tracheal stenosis, certain types of tumors that invade the airway, trauma or an inhaled piece of food or small object that is trapped in the airway. Medical History Your NYU Langone's doctor may ask you to describe when you first noticed noisy breathing, whether the sound comes and goes or is consistent, and if you are disturbing your daily activities, such as eating and sleeping. Physical examYour doctor may examine your face, neck, and throat to detect signs of a blocked airway. The doctor can also hear your breathing with a stethoscope, an instrument used to magnify sounds in the lungs and the airway. You can also look for signs of infection, which can cause inflammation in your throat. Flexible laryngoscopySplit larynxoscopy Flexible larynxoscopy helps a doctor to examine the airway and vocal cords. Doctors use the procedure to determine whether the airway is narrow and, if so, identify the cause. This test takes place in the doctor's office and takes about five minutes. To perform the procedure, your doctor first uses a local anesthetic spray to numb your nose and throat. Then insert an endoscope — a very thin and flexible instrument with a high definition video camera and light at the end — into a nose and airway. The camera helps identify any narrowing, obstruction or other anomalies. X-ray If your doctor thinks the cause of the stridor is a foreign object, such as a piece of food you have ingested or inhaled, he or she may recommend a . X-ray creates detailed images of structures within the body and can show an object hosted on the airway or lungs. CT ScansA is a type of X-ray that produces detailed, three-dimensional and cross-sectional images of tissues and organs, which are displayed on a computer monitor. These scans can help a doctor determine whether a tumor, vocal cord paralysis, or subglottic or tracheal stenosis is the cause of the stridor. BronchoscopyBronchoscopic bronchoscopy is a test of the airway and the lungs using a bronchoscope, a long, thin instrument with a camera at the tip. A doctor may recommend a bronchoscopy if an X-ray shows an ingested or inhaled object. Specialists use general anesthesia for this test to reduce any discomfort. To perform this test, your doctor inserts the bronchoscope through your nose or mouth and lungs. The range sends a clear picture of the airway and the lungs to a monitor and helps doctors determine if an object is blocking the airflow. If the bronchoscope reveals that an object is present, the doctor may pass small surgical instruments through the bronchoscope to remove it. ElectromyographyElectromyography, or EMG, measures the electrical impulses that run through nerves, nerve roots and muscles, testing how well nerves and muscles work together. Your doctor may perform EMG to determine if there is any nerve or muscle dysfunction in the larynx, or voice box. To perform this test, the doctor inserts a small needle, called electrode, into a muscle in the throat. This allows your doctor to measure the amount of electrical muscle cells that generate when activated by a nervous impulse. In people who have stridor, muscle fibers may not respond, as well as usually muscles work. Our Research and Education in Adult Stridor Learn more about our research and vocational education opportunities. We can help you find a doctor. Call or . Explore NYU Langone

Is Your Nose Working Against You? 5 Signs of a Deviated Septum – Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic

Stridor (Noisy Breathing) - Pediatric Pulmonologists
Every time I breathe out through my nose, I can hear a squeaking noise coming from my nose. Why is that? - Quora
noisy breathing | Dr Annabelle Leong

Why does my nose whistle? - Oakdale ENT

How to Be a Nose Breather - The New York Times

Upper airway
![6 signs you have a deviated septum [Infographic] 6 signs you have a deviated septum [Infographic]](https://drmonicatadros.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/6-signs-you-have-a-deviated-septum-2.png)
6 signs you have a deviated septum [Infographic]

Noisy Breathing in Kids

Laryngomalacia (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth

Mouth breathing: Causes, symptoms, and complications

4 Signs You Should See a Doctor for Your Deviated Septum | | Keck Medicine of USC
Noisy Breathing in Adults: Causes & Symptoms | Breathing.com
Breath sounds: Abnormal breathing and treatment
Labored Breathing in Toddlers: Causes, Symptoms, When to Go to the ER

Does Your Nose Whistle When You Breathe?

Deviated Septum: Symptoms, Causes and Treatments

Mouth breathing: Causes, symptoms, and complications

Mouth Breathing: Symptoms, Complications, and Treatments

Noisy baby breathing: What's normal and what's not - Kidspot

Stridor Versus Wheezing: When Noisy Breathing Is Something More | Johns Hopkins Medicine

Deviated Septum: Symptoms, Causes and Treatments

Breathing Difficulties in Cats - Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Recovery, Management, Cost

Newborn Snoring: Why Does This Happen?
Noisy Baby Breathing
/107797082-56a17a5d3df78cf7726b0a0b.jpg)
Wheezing as a Sign of Respiratory Distress

Why is my baby's breathing so noisy | Bounty

Heavy Breathing: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and More

Does your child have noisy breathing? | Texas Children's Hospital

Noisy Breathing in Cats - Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Recovery, Management, Cost

Newborne Breathing Noises: Whats Normal & What's Not

Deviated Septum: Symptoms, Causes and Treatments

Mouth Breathing: Physical, Mental and Emotional Consequences

Noisy Breathing in Dogs - Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Recovery, Management, Cost

What Are The Common Causes Of Snoring by michaelsjulia260 - issuu

Stridor Versus Wheezing: When Noisy Breathing Is Something More | Johns Hopkins Medicine

Noisy baby breathing: What's normal and what's not - Kidspot

Snoring with an Open Mouth - SnoreLab Insights

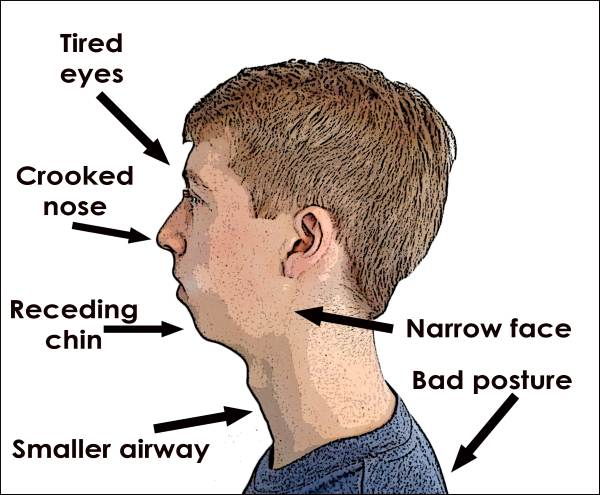
Why Your Child's Mouth Breathing Should Worry You - Dr. Michael Gelb

Laryngomalacia: Is My Child's Noisy Breathing Serious? - Cincinnati Children's Blog
Posting Komentar untuk "loud breathing through nose"